Introduction
SafeBreach Labs discovered a new vulnerability in Trend Micro Password Manager software.
In this post, we will demonstrate how this vulnerability could have been used in order to achieve privilege escalation and persistence by loading an arbitrary unsigned DLL into a service that runs as NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM.
Trend Micro Password Manager
Trend Micro Password Manager is a standalone software which is also deployed along with the Trend Micro Maximum Security product. The purpose of the software is to manage website passwords and login IDs in one secure location.
Part of the software runs as a Windows service executed as “NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM,” which provides it with very powerful permissions.
In this post, we describe the vulnerability we found in the Trend Micro Password Manager.
We then demonstrate how this vulnerability can be exploited to achieve privilege escalation, gaining access with NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM level privileges.
Vulnerability
Discovery
In our initial exploration of the software, we targeted the “Trend Micro Password Manager Central Control Service” (PwmSvc.exe), because:
- It runs as NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM – the most privileged user account. This kind of service might be exposed to a user-to-SYSTEM privilege escalation, which is very useful and powerful to an attacker.
- The executable of the service is signed by Trend Micro and if the hacker finds a way to execute code within this process, it can be used as an application whitelisting bypass.
- This service automatically starts once the computer boots, which means that it’s a potential target for an attacker to be used as a persistence mechanism.
In our exploration, we found that after the Trend Micro Password Manager Central Control Service was started, the PwmSvc.exe signed process was executed as NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM.
Once executed, the service loaded the “Trend Micro White List Module” library tmwlutil.dll and we noticed an interesting behavior:

As you can see, the service was trying to load a missing DLL file, which eventually was loaded from the c:\python27 directory – a directory within our PATH environment variable.
Stay with us, we will analyze the root cause in the next section of the article.
PoC Demonstration
In our VM, the c:\python27 has an ACL which allows any authenticated user to write files onto the ACL. This makes the privilege escalation simple and allows a regular user to write the missing DLL file and achieve code execution as NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM.
It is important to note that an administrative user or process must (1) set the directory ACLs to allow access to non-admin user accounts, and (2) modify the system’s PATH variable to include that directory. This can be done by different applications.
In order to test this privilege escalation vulnerability, we compiled a DLL (unsigned) which writes the following to the filename of a txt file:
- The name of the process which loaded it
- The username which executed it
- The name of the DLL file
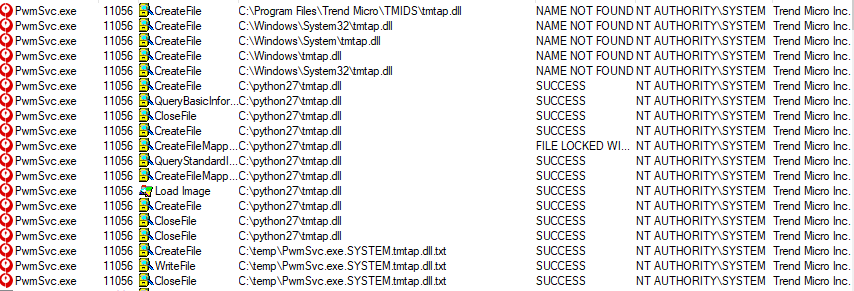
**
We were able to load an arbitrary DLL as a regular user and execute our code within a process which is signed by Trend Micro as NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM.**
Root Cause Analysis
Once the “Trend Micro Whitelist Module” library tmwlutil.dll is loaded, it initializes a class called “TAPClass”, which, in turn, tries to load another library called “tmtap.dll”
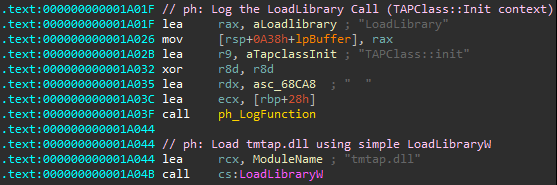
There are two root causes for the vulnerability:
- Uncontrolled Search Path – The lack of safe DLL loading.
The library tried to load the mentioned DLL files using LoadLibraryW. The problem is that it used only the filename of the DLL, instead of an absolute path. In this case, it’s necessary to use the SetDefaultDllDirectories and/or LoadLibraryExW functions in order to control the paths from which the DLL will be loaded. - No digital certificate validation is made against the binary. The program doesn’t validate whether the DLL that it is loading is signed (e.g. using the WinVerifyTrust function). Therefore, it can load an arbitrary unsigned DLL.
Potential Malicious Uses and Impact
Trend Micro Password Manager is deployed with the Trend Micro Maximum Security Software.
Below we show two possible ways that an attacker can leverage the vulnerability we discovered and documented above.
Signed Execution and Whitelisting Bypass
The vulnerability gives attackers the ability to load and execute malicious payloads using a signed service. This ability might be abused by an attacker for different purposes such as execution and evasion, for example: Application Whitelisting Bypass.
Persistence Mechanism
The vulnerability gives attackers the ability to load and execute malicious payloads in a persistent way, each time the service is being loaded. That means that once the attacker drops a malicious DLL in a vulnerable path, the service will load the malicious code each time it is restarted.
Privilege Escalation
After an attacker gains access to a computer, he might have limited privileges which can limit his operations to access certain files and data. The service provides him with the ability to operate as NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM which is the most powerful user in Windows, so he can access almost every file and process which belongs to the user on the computer.
Affected Versions
- Trend Micro Maximum Security / Password Manager 15.0.0.1229
- Trend Micro Password Manager Service
(PwmSvc.exe)– 3.8.0.1069 - Tmwlutil.dll 2.97.0.1161
Timeline
July 23th, 2019 – Vulnerability reported to Trend Micro
July 24th, 2019 – Initial Response from Trend Micro
July 31th, 2019 – Status Update from Trend Micro
July 31th, 2019 – Trend Micro resolved the issue and released a new version.
Aug 13th, 2019 – Trend Micro has issued CVE-2019-14684
Apr 14th, 2019 – Trend Micro has published a security bulletin: http://esupport.trendmicro.com/en-us/home/pages/technical-support/1123396.aspx