SafeBreach Labs has updated the Hacker’s Playbook™ with new simulations for malware samples described in US-CERT Guidance on the North Korean Cyber Threat (AA20-106A) which addresses the troubling and destructive attacks from the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK), aka Hidden Cobra.
The North Korean threat groups are notorious for devastating attacks, including the infamous WannaCry attack in 2017 from Lazarus Group, the attack against Sony Pictures in 2014 in retaliation for ‘The Interview’ film by Guardians of Peace, and the Bangladesh Bank Heist in 2016 where \$81 million was stolen via the SWIFT network, among others.
The alert also details alarming activity over the past year including: cyber-enabled financial theft and money laundering, extortion campaigns, and cryptojacking. It is clear the DPRK is attacking for financial gain, with estimated thefts of \$2 billion to date.
The alert notes the primary goal of the DPRK is to destabilize financial systems across the globe, but it also addresses their capability to conduct disruptive or destructive cyber activities affecting U.S. critical infrastructure. (e.g., Chemical, Communications, Dams, Emergency Services, Financial Services, Government Facilities, Transportation Systems, Financial Institutions, Critical Manufacturing, Defense Industrial Base, Energy, Food and Agriculture, Healthcare, Nuclear Reactors and Water Systems)
The SafeBreach Hacker’s Playbook addresses the wide array of attacks noted throughout the alert to keep your organization safe.
Newly developed playbook methods related to AA20-106A:
- #4224 – Write BISTROMATH malware to disk (Host-Level)
- #4225 – Transfer of BISTROMATH malware over HTTP/S (Lateral Movement
- #4226 – Transfer of BISTROMATH malware over HTTP/S (Infiltration)
- #4227 – Email BISTROMATH malware as a ZIP attachment (Lateral Movement)
- #4228 – Email BISTROMATH malware as a ZIP attachment (Infiltration)
- #4229 – Write SLICKSHOES malware to disk (Host-Level)
- #4230 – Transfer of SLICKSHOES malware over HTTP/S (Lateral Movement)
- #4231 – Transfer of SLICKSHOES malware over HTTP/S (Infiltration)
- #4232 – Email SLICKSHOES malware as a ZIP attachment (Lateral Movement)
- #4233 – Email SLICKSHOES malware as a ZIP attachment (Infiltration)
- #4234 – Write CROWDEDFLOUNDER malware to disk (Host-Level)
- #4235 – Transfer of CROWDEDFLOUNDER malware over HTTP/S (Lateral Movement)
- #4236 – Transfer of CROWDEDFLOUNDER malware over HTTP/S (Infiltration)
- #4237 – Email CROWDEDFLOUNDER malware as a ZIP attachment (Lateral Movement)
- #4238 – Email CROWDEDFLOUNDER malware as a ZIP attachment (Infiltration)
- #4239 – Write HOTCROISSANT malware to disk (Host-Level)
- #4240 – Transfer of HOTCROISSANT malware over HTTP/S (Lateral Movement)
- #4241 – Transfer of HOTCROISSANT malware over HTTP/S (Infiltration)
- #4242 – Email HOTCROISSANT malware as a ZIP attachment (Lateral Movement)
- #4243 – Email HOTCROISSANT malware as a ZIP attachment (Infiltration)
- #4244 – Write ARTFULPIE malware to disk (Host-Level)
- #4245 – Transfer of ARTFULPIE malware over HTTP/S (Lateral Movement)
- #4246 – Transfer of ARTFULPIE malware over HTTP/S (Infiltration)
- #4247 – Email ARTFULPIE malware as a ZIP attachment (Lateral Movement)
- #4248 – Email ARTFULPIE malware as a ZIP attachment (Infiltration)
- #4249 – Write BUFFETLINE malware to disk (Host-Level)
- #4250 – Transfer of BUFFETLINE malware over HTTP/S (Lateral Movement)
- #4251 – Transfer of BUFFETLINE malware over HTTP/S (Infiltration)
- #4252 – Email BUFFETLINE malware as a ZIP attachment (Lateral Movement)
- #4253 – Email BUFFETLINE malware as a ZIP attachment (Infiltration)
- #4254 – Write DeltaCharlie malware to disk (Host-Level)
- #4255 – Transfer of DeltaCharlie malware over HTTP/S (Lateral Movement)
- #4256 – Transfer of DeltaCharlie malware over HTTP/S (Infiltration)
- #4257 – Email DeltaCharlie malware as a ZIP attachment (Lateral Movement)
- #4258 – Email DeltaCharlie malware as a ZIP attachment (Infiltration)
Existing playbook methods related to AA20-106A:
- 2252- “Write Trojan-Hoplight malware to disk”,
- 2253 – “Transfer of Trojan-Hoplight malware over HTTP/S”,
- 2254 – “Transfer of Trojan-Hoplight malware over HTTP/S”,
- 2255 – “Email Trojan-Hoplight malware as a ZIP attachment”,
- 2256 – “Email Trojan-Hoplight malware as a ZIP attachment”,
- 2257 – “Write Trojan-Hoplight (rdpproto) malware to disk”,
- 2258 – “Transfer of Trojan-Hoplight (rdpproto) malware over HTTP/S”,
- 2259 – “Transfer of Trojan-Hoplight (rdpproto) malware over HTTP/S”,
- 2260 – “Email Trojan-Hoplight (rdpproto) malware as a ZIP attachment”,
- 2261 – “Email Trojan-Hoplight (rdpproto) malware as a ZIP attachment”,
- 2383 – “Write HOPLIGHT (AR19-304A) malware to disk”,
- 2384 – “Transfer of HOPLIGHT (AR19-304A) malware over HTTP/S”,
- 2385 – “Transfer of HOPLIGHT (AR19-304A) malware over HTTP/S”,
- 2386 – “Email HOPLIGHT (AR19-304A) malware as a ZIP attachment”,
- 2387 – “Email HOPLIGHT (AR19-304A) malware as a ZIP attachment”,
- 2689 – “Write hoplight malware to disk”,
- 2690 – “Transfer of hoplight malware over HTTP/S”,
- 2691 – “Transfer of hoplight malware over HTTP/S”,
- 2692 – “Email hoplight malware as a ZIP attachment”,
- 2693 – “Email hoplight malware as a ZIP attachment”,
- 3114 – “Pre-execution phase of HOPLIGHT (AR19-304A) malware”,
- 3148 – “Pre-execution phase of hoplight malware”,
- 801 – “Lazarus Fake TLS”
- 2287 – “Write ELECTRICFISH malware to disk”,
- 2288 – “Transfer of ELECTRICFISH malware over HTTP/S”,
- 2289 – “Transfer of ELECTRICFISH malware over HTTP/S”,
- 2290 – “Email ELECTRICFISH malware as a ZIP attachment”,
- 2291 – “Email ELECTRICFISH malware as a ZIP attachment”,
- 2292 – “Communication with Proxy Server using ELECTRICFISH Authentication Protocol (AR19-129A)”,
- 3110 – “buffer”, – “Pre-execution phase of ELECTRICFISH malware”,
- 1481 – “Transfer of BADCALL malicious file over HTTP/S”,
- 1482 – “Transfer of BADCALL malicious file over HTTP/S”,
- 1483 – “Drop to disk BADCALL malicious file”,
- 1484 – “Transfer of the BadCall Malware over HTTP/S”,
- 1485 – “Transfer of the BadCall Malware over HTTP/S”,
- 1486 – “Write Badcall to Disk”,
- 1881 – “Email the BADCALL malware as part of a ZIP attachment”,
- 2083 – “Email the BADCALL malware as part of a ZIP attachment”,
- 2370 – “Pre-execution phase of BADCALL malware”,
- 3081 – “Pre-execution phase of Badcall malware”,
- 3288 – Write badcall malware to disk”,
- 3289 – “Transfer of badcall malware over HTTP/S”,
- 3290 – “Transfer of badcall malware over HTTP/S”,
- 3291 – “Email badcall malware as a ZIP attachment”,
- 3292 – “Email badcall malware as a ZIP attachment”,
- 1666 – “Write FASTCash (TA18-275A) malware to Disk”,
- 1667 – “Transfer of Fastcash malicious file over Email”,
- 1668 – “Transfer of the FASTCash Malware over HTTP/s”,
- 1669 – “Transfer of Fastcash malicious file over HTTP/S”,
- 1675 – “Email FASTCash (TA18-275A) malware inside a ZIP attachment”,
- 1678 – “Email FASTCash (TA18-275A) malware inside a ZIP attachment”,
- 3095 – “buffer”, “Pre-execution phase of FASTCash (TA18-275A) malware”,
- 1622 – “Write KEYMARBLE Trojan to disk”,
- 1623 – “malware_buffer”, “Transfer of the KeyMarble Trojan over HTTP/s”,
- 1896 – “Email the KEYMARBLE malware as part of a ZIP attachment”,
- 2098 – “Email the KEYMARBLE malware as part of a ZIP attachment”,
- 2744 – “Write keymarble malware to disk”,
- 2745 – “Transfer of keymarble malware over HTTP/S”,
- 2746 – “Transfer of keymarble malware over HTTP/S”,
- 2747 – “Email keymarble malware as a ZIP attachment”,
- 2748 – “Email keymarble malware as a ZIP attachment”,
- 3091 – “buffer”, “Pre-execution phase of KEYMARBLE Trojan malware”,
- 3156 – “buffer”, “Pre-execution phase of keymarble malware”,
- 4105 – “Email the KEYMARBLE malware as part of a coronavieus campaign as ZIP attachment”,
- 3015 – “Write typeframe malware to disk”,
- 3016 – “Transfer of typeframe malware over HTTP/S”,
- 3017 – “Transfer of typeframe malware over HTTP/S”,
- 3018 – “Email typeframe malware as a ZIP attachment”,
- 3019 – “Email typeframe malware as a ZIP attachment”,
- 3193 – “Pre-execution phase of typeframe malware”,
- 1564 – “Transfer of Joanap/Brambul (TA18-149A) files over HTTP/S”,
- 1565 – “Write Joanap/Brambul (TA18-149A) files to Disk”,
- 1567 – “Transfer of Dropper (Joanap/Brambul) over HTTP/S”,
- 1568 – “Transfer of Joanap/Brambul (TA18-149A) files over HTTP/S – Duplicated”,
- 1569 – “Transfer of Joanap/Brambul (TA18-149A) files over HTTP/S – Duplicated”,
- 1890 – “Email the Joanap/Brambul (TA18-149A) files malware as part of a ZIP attachment”,
- 2092 – “Email the Joanap/Brambul (TA18-149A) files malware as part of a ZIP attachment”,
- 3086 – “Pre-execution phase of Joanap/Brambul (TA18-149A) files malware”,
- 2664 – “Write hardrain malware to disk”,
- 2665 – “Transfer of hardrain malware over HTTP/S”,
- 2666 – “name”: “Transfer of hardrain malware over HTTP/S”,
- 2667 – “Email hardrain malware as a ZIP attachment”,
- 2668 – “Email hardrain malware as a ZIP attachment”,
- 3293 – “Pre-execution phase of bankshot malware”,
- 3294 – “Write bankshot malware to disk”,
- 3295 – “Transfer of bankshot malware over HTTP/S”,
- 3296 – “Transfer of bankshot malware over HTTP/S”,
- 3297 – “Email bankshot malware as a ZIP attachment”,
- 3298 – Email bankshot malware as a ZIP attachment”,
- 1412 – “Transfer of the FallChill RAT over HTTP”,
- 1413 – “Write FALLCHILL RAT (TA17-318A) to Disk”,
- 1425 – “FALLCHILL – Communication with C&C using TLS”,
- 1876 – “Email the FALLCHILL RAT (TA17-318A) as part of a ZIP attachment”,
- 2078 – “Email the FALLCHILL RAT (TA17-318A) as part of a ZIP attachment”,
- 2573 – “Write fallchill malware to disk”,
- 2574 – “Transfer of fallchill malware over HTTP/S”,
- 2575 – “Transfer of fallchill malware over HTTP/S”,
- 2576 – “Email fallchill malware as a ZIP attachment”,
- 2577 – “Email fallchill malware as a ZIP attachment”,
- 3077 – “Pre-execution phase of FALLCHILL RAT (TA17-318A) malware”,
- 3137 – “Pre-execution phase of fallchill malware”
- 1414 – “Transfer of the Volgmer Trojan over HTTP”,
- 1415 – “Write Volgmer Trojan (TA17-318B) to Disk”,
- 1877 – “name”: “Email the Volgmer malware (TA17-318B) as part of a ZIP attachment”,
- 2079 – “Email the Volgmer (TA17-318B) malware as part of a ZIP attachment”,
- 2368 – “Pre-execution phase of Volgmer malware”,
- 3078 – “Pre-execution phase of Volgmer Trojan (TA17-318B) malware”,
- 1292 – “Write WannaCry 2.0 Ransomware to Disk”
- 1293 – “Transfer of WannaCry 2.0 ransomware over HTTP/S”,
- 2364 – “Pre-execution phase of WannaCry 2.0 malware”,
Recommendations:
As North Korean threat groups are notorious for ransomware, e.g., WannaCry. The SafeBreach Hacker’s Playbook has attack methods for over 100 different types of ransomware that we recommend you include in your testing for this specific US-CERT alert.
Measures to Counter DPRK (aka Hidden Cobra) Cyber Threats:
U.S. Department of Homeland Security – CISA calls out that it is imperative that we:
- Share technical information of the DPRK cyber threat. Here is the quick link to access the CISA Information Sharing and Awareness.
- Implement and promote cybersecurity best practices. As a user of SafeBreach you have at your disposal over 400 breach and attack methods that simulate the threat groups associated with DPRK.
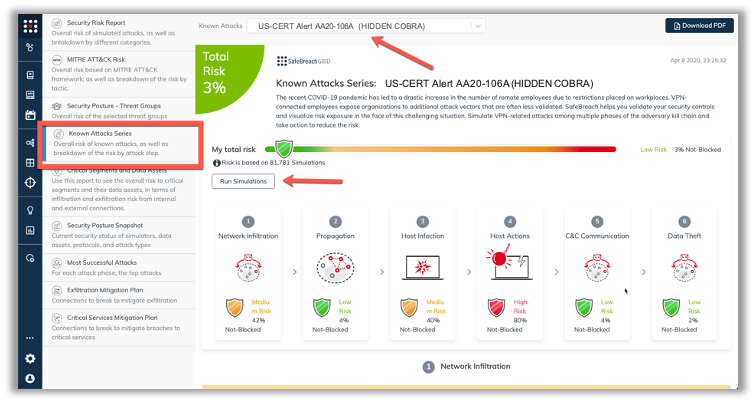
The new attack methods for US-CERT AA20-106A are already in the SafeBreach Hacker’s Playbook and ready to be run across your simulators. The Known Attack Series report is being updated so you can run only the attacks from this US-CERT alert. From the Known Attack Series report, select the US-CERT Alert AA20-106A (HIDDEN COBRA) report and there is an option to Run Simulations which will run all the attacks methods.